The Philosophy of Education: Shaping Minds, Building Futures
Education is not just about acquiring knowledge; it is a transformative experience that shapes individuals and societies. At the core of education lies a philosophy that guides how we teach, learn, and understand the world around us.
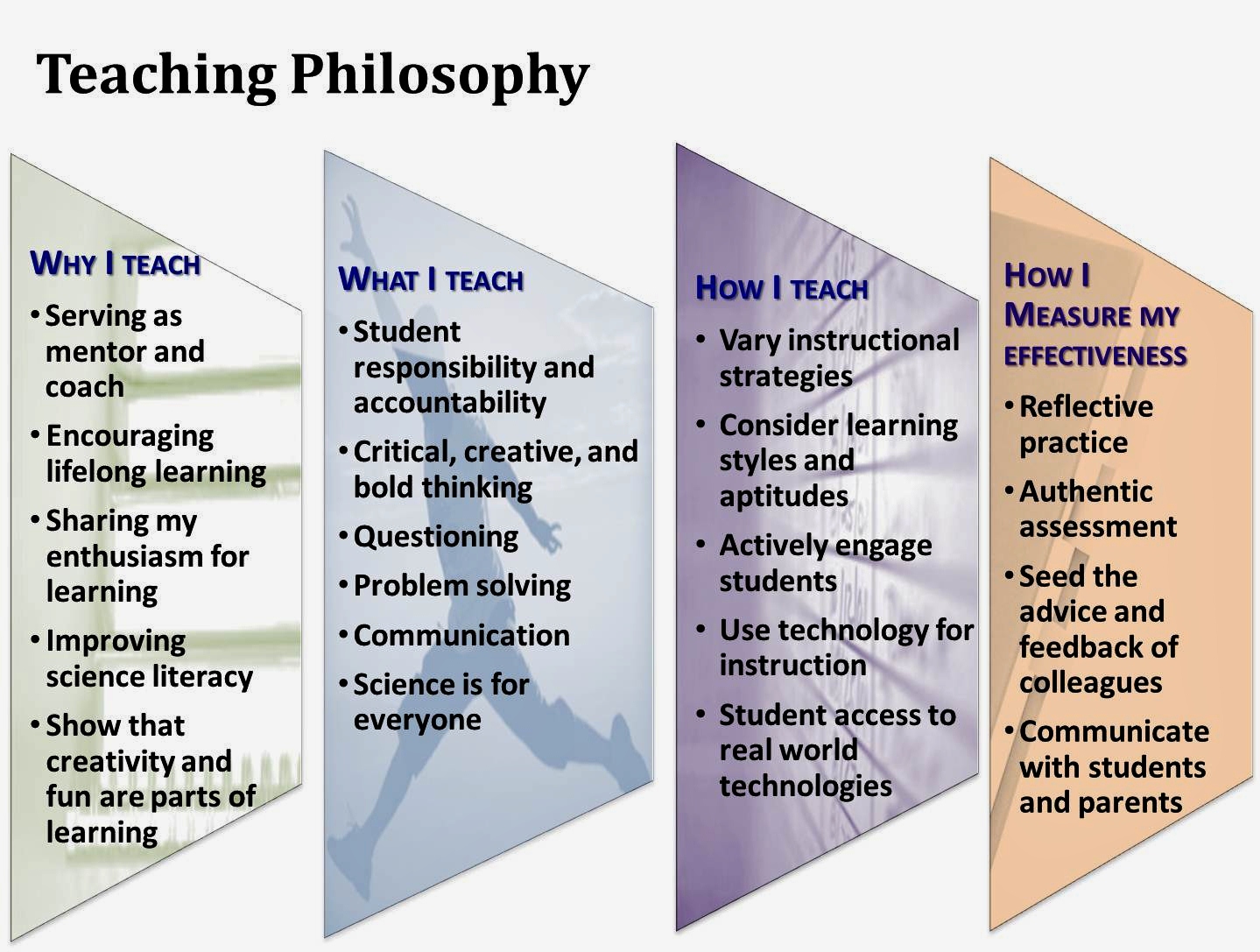
Defining Philosophy of Education
The philosophy of education encompasses the beliefs, values, and principles that underpin educational practices. It explores fundamental questions such as:
- What is the purpose of education?
- How do we define knowledge and truth?
- What is the role of teachers and students in the learning process?
- How should educational institutions be structured?
Key Philosophies in Education
There are various philosophies that have influenced educational thought throughout history:
- Perennialism: Emphasizes universal truths and enduring ideas as the foundation of education.
- Progressivism: Focuses on experiential learning, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills.
- Constructivism: Advocates for active learning through hands-on experiences and social interactions.
- Humanism: Places importance on individual growth, self-actualization, and personal development.
The Impact of Philosophy on Education
The philosophy of education shapes curriculum design, teaching methods, assessment practices, and overall educational goals. It influences how educators approach instruction, classroom management, student engagement, and fostering a love for lifelong learning.
In Conclusion
Exploring the philosophy of education allows us to reflect on the purpose and meaning of learning. By understanding different educational philosophies, we can create enriching learning environments that nurture intellectual curiosity, creativity, critical thinking skills, and a deep appreciation for knowledge.
Exploring Key Questions About the Philosophy of Education
- What are the 5 major philosophy of education?
- What is the philosophy of your education?
- What are the 7 philosophy of education and meaning?
- What are the 7 philosophies of education?
- What is an example of a philosophy of education?
- What is the philosophy of education?
What are the 5 major philosophy of education?
The question “What are the 5 major philosophies of education?” is a common inquiry that highlights the diverse approaches and beliefs that shape educational practices. The five major philosophies of education include perennialism, progressivism, essentialism, existentialism, and social reconstructionism. Each philosophy offers a unique perspective on the purpose of education, the role of teachers and students, and the methods of teaching and learning. By understanding these foundational philosophies, educators can gain insight into different pedagogical approaches and tailor their teaching practices to meet the needs and goals of their students.
What is the philosophy of your education?
The philosophy of education at our institution is rooted in the belief that learning should be a transformative and empowering experience for all individuals. We embrace a student-centered approach that values critical thinking, creativity, and lifelong learning. Our educational philosophy focuses on fostering a supportive and inclusive environment where students are encouraged to explore diverse perspectives, engage in collaborative learning experiences, and develop the skills needed to navigate an ever-changing world. Through our commitment to excellence, innovation, and personal growth, we aim to inspire a passion for knowledge and empower students to reach their full potential.
What are the 7 philosophy of education and meaning?
The question “What are the 7 philosophies of education and their meanings?” is a common inquiry that seeks to understand the diverse perspectives that shape educational practices. The seven main philosophies of education include perennialism, essentialism, progressivism, social reconstructionism, existentialism, behaviorism, and constructivism. Each philosophy offers a unique approach to teaching and learning, emphasizing different values, beliefs, and methodologies. Perennialism focuses on universal truths and classical knowledge, essentialism prioritizes core academic subjects and traditional values, progressivism promotes experiential learning and student-centered approaches, social reconstructionism advocates for social change through education, existentialism emphasizes individual freedom and self-discovery, behaviorism focuses on observable behaviors and conditioning techniques, while constructivism highlights active learning and knowledge construction through experiences. Understanding these philosophies helps educators shape their teaching practices to best meet the needs of their students while fostering a holistic approach to education.
What are the 7 philosophies of education?
There are seven key philosophies of education that have significantly influenced educational thought and practice. These philosophies include perennialism, progressivism, essentialism, existentialism, behaviorism, constructivism, and humanism. Each philosophy offers a unique perspective on the purpose of education, the role of teachers and students, and the methods used for teaching and learning. By understanding these diverse philosophies of education, educators can tailor their approaches to better meet the needs and goals of their students while fostering a rich and engaging learning environment.
What is an example of a philosophy of education?
One example of a philosophy of education is progressivism, which emphasizes experiential learning, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills. In a progressive educational approach, students are encouraged to actively engage with the material through hands-on experiences and collaborative activities. Teachers serve as facilitators who guide students in exploring their interests, fostering creativity, and developing a deeper understanding of the world around them. Progressivism values student-centered learning, individual growth, and the application of knowledge in real-world contexts, aiming to prepare students for active participation in society and lifelong learning.
What is the philosophy of education?
The philosophy of education delves into the fundamental beliefs and principles that shape our approach to teaching and learning. It seeks to answer profound questions about the purpose of education, the nature of knowledge, the roles of teachers and students, and the structure of educational institutions. Essentially, the philosophy of education serves as a guiding framework that influences curriculum design, instructional methods, assessment practices, and overall educational objectives. By exploring the philosophy of education, we gain insight into the underlying values that drive our educational endeavors and strive to create meaningful and impactful learning experiences for individuals and society as a whole.