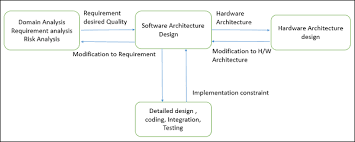
Understanding Software Architecture
Software architecture is a crucial aspect of software development that defines the structure and behavior of a system. It serves as the blueprint for designing, building, and maintaining software applications.
Key Components of Software Architecture
Software architecture consists of several key components:
- Components: These are the modular units of a system that encapsulate its functionality.
- Interfaces: These define how components interact with each other.
- Architectural Patterns: These are reusable solutions to common design problems.
- Data Management Strategies: These define how data is stored, accessed, and managed within the system.
- Deployment Strategies: These determine how the system will be deployed and run in various environments.
The Importance of Software Architecture
A well-designed software architecture provides several benefits:
- Maintainability: A clear architecture makes it easier to maintain and update the system over time.
- Scalability: A scalable architecture allows the system to grow and adapt to changing requirements.
- Performance: An optimized architecture can improve the performance of the system.
- Sustainability: A sustainable architecture ensures the long-term viability of the software product.
Common Architectural Styles
There are several common architectural styles used in software development, including:
- MVC (Model-View-Controller): Separates an application into three main components for managing user interfaces, data, and business logic.
- Microservices: Decomposes an application into smaller, independent services that can be developed and deployed separately.
9 Essential Tips for Building Robust and Scalable Software Architecture
- Separate concerns to improve maintainability
- Use design patterns to solve common problems
- Keep the architecture flexible for future changes
- Document the architecture and design decisions
- Consider performance implications in the design
- Ensure scalability to handle growing user loads
- Implement security measures at all levels of the architecture
- Encourage modularity for easier testing and debugging
- Regularly review and refactor the architecture for optimization
Separate concerns to improve maintainability
When designing software architecture, it is essential to separate concerns to improve maintainability. By dividing the system into distinct modules or components, each responsible for a specific aspect of functionality, developers can isolate changes and updates to specific areas without affecting the entire system. This approach simplifies maintenance tasks, reduces the risk of unintended consequences, and makes it easier to understand and modify the software over time. Separating concerns also promotes code reusability and enhances collaboration among team members working on different parts of the system. Ultimately, by prioritizing the separation of concerns in software architecture, developers can create more robust and adaptable applications that are easier to manage and evolve.
Use design patterns to solve common problems
In software architecture, utilizing design patterns is a valuable strategy to address common problems that arise during the development process. Design patterns offer proven solutions to recurring design challenges, allowing developers to leverage established best practices and principles in their software designs. By incorporating design patterns into the architecture, developers can improve code quality, enhance maintainability, and promote reusability across different parts of the system. This approach not only streamlines the development process but also fosters consistency and scalability in software projects.
Keep the architecture flexible for future changes
Keeping the software architecture flexible for future changes is a crucial tip in software development. By designing an architecture that can easily adapt to evolving requirements and technologies, developers can save time and effort in the long run. A flexible architecture allows for seamless integration of new features, updates, and enhancements without requiring a complete overhaul of the system. This approach not only future-proofs the software but also ensures its scalability and maintainability over time.
Document the architecture and design decisions
Documenting the architecture and design decisions is a crucial tip in software architecture. By documenting these aspects, developers can create a comprehensive record of the system’s structure, components, and interactions. This documentation serves as a valuable reference for future development, maintenance, and troubleshooting efforts. It also helps new team members understand the rationale behind design choices and facilitates communication among stakeholders. Overall, thorough documentation of architecture and design decisions promotes transparency, consistency, and scalability in software development projects.
Consider performance implications in the design
When designing software architecture, it is essential to consider the performance implications of your decisions. By taking into account how the design choices may impact the system’s performance, you can proactively address potential bottlenecks and optimize the overall efficiency of the software. Factors such as response time, throughput, resource utilization, and scalability should be carefully evaluated during the design phase to ensure that the final system meets performance requirements and delivers a smooth user experience. Prioritizing performance considerations in the design process can lead to a more robust and reliable software solution in the long run.
Ensure scalability to handle growing user loads
Ensuring scalability in software architecture is crucial to handle growing user loads effectively. By designing a scalable system, software developers can ensure that the application can accommodate increased user traffic without compromising performance or reliability. Scalability allows the system to expand its capacity seamlessly as the user base grows, ensuring a smooth user experience and preventing downtime or performance issues. Implementing scalable architecture principles such as load balancing, horizontal scaling, and efficient resource management can help future-proof the software application and support its growth over time.
Implement security measures at all levels of the architecture
Implementing security measures at all levels of the architecture is a crucial tip in software development. By incorporating security considerations from the initial design phase through implementation and maintenance, developers can create a robust and secure system. This approach helps in safeguarding sensitive data, protecting against potential threats, and ensuring the overall integrity of the software application. By addressing security at every level of the architecture, developers can build trust with users and stakeholders while mitigating risks associated with cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
Encourage modularity for easier testing and debugging
Encouraging modularity in software architecture is a valuable tip that can greatly enhance the testing and debugging processes. By breaking down a system into smaller, independent modules, each responsible for a specific functionality, developers can isolate and test individual components more effectively. This approach not only simplifies the testing process but also makes debugging easier as issues can be pinpointed to specific modules rather than navigating through a monolithic codebase. Modularity promotes code reusability, maintainability, and scalability, ultimately leading to more robust and reliable software systems.
Regularly review and refactor the architecture for optimization
Regularly reviewing and refactoring the architecture of a software system is essential for optimizing its performance and maintainability. By periodically assessing the design and structure of the system, developers can identify areas for improvement, eliminate inefficiencies, and ensure that the architecture aligns with current best practices. Refactoring allows for streamlining code, improving scalability, enhancing security, and overall making the system more robust and adaptable to future changes. This proactive approach to software architecture not only enhances the quality of the system but also reduces technical debt and minimizes risks associated with outdated or inefficient design choices.
Categories: