Whole Brain Teaching: A Holistic Approach to Education
In today’s rapidly changing world, traditional teaching methods may no longer be sufficient to engage and inspire students. As educators strive to create dynamic learning environments, they are turning to innovative approaches like Whole Brain Teaching (WBT) to enhance student engagement, foster critical thinking skills, and promote holistic development.
So, what exactly is Whole Brain Teaching? It is an instructional strategy that aims to activate all areas of the brain simultaneously during the learning process. By engaging both the logical and creative sides of the brain, WBT creates a more comprehensive learning experience for students.
One of the key principles of Whole Brain Teaching is active participation. Instead of passively listening to lectures or reading textbooks, students are encouraged to actively engage in their own learning. This approach involves using gestures, movement, and verbalization techniques that stimulate different parts of the brain.
By incorporating physical movement into lessons, WBT taps into kinesthetic learning, which helps students retain information more effectively. For example, teachers might ask students to perform specific hand motions while reciting key concepts or use body movements to represent mathematical operations. These actions stimulate neural connections in multiple areas of the brain simultaneously.
Another important aspect of Whole Brain Teaching is its emphasis on immediate feedback and reinforcement. In traditional teaching methods, feedback often comes after assignments or exams have been graded. However, with WBT, teachers provide instant feedback during lessons through various techniques such as call-and-response activities or “mirroring” exercises where students repeat information back to their peers.
This real-time feedback helps students gauge their understanding instantly and correct any misconceptions on the spot. It also promotes active listening skills as students need to pay attention in order to respond appropriately during these interactive activities.
Moreover, Whole Brain Teaching recognizes that emotions play a crucial role in learning. By creating a positive and supportive classroom environment, educators can foster emotional connections that enhance student motivation and engagement. WBT encourages teachers to establish strong relationships with their students, using humor, enthusiasm, and empathy to create a safe and inclusive space for learning.
Through the use of Whole Brain Teaching techniques, educators can address the diverse learning styles and preferences of their students. By engaging both hemispheres of the brain, WBT caters to visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners alike. This approach ensures that all students have an opportunity to thrive in the classroom and reach their full potential.
In conclusion, Whole Brain Teaching is an innovative educational approach that harnesses the power of active participation, immediate feedback, and emotional connections to create a holistic learning experience. By engaging all areas of the brain simultaneously, this method promotes deeper understanding, critical thinking skills, and overall student success. As educators continue to explore new ways to enhance teaching and learning outcomes, Whole Brain Teaching stands out as a promising strategy that nurtures well-rounded learners in today’s ever-evolving world.
Frequently Asked Questions about Whole Brain Teaching: Rule #1, The Big 7, The 5 Virtues, and an Overview
- What is the rule #1 in whole brain teaching?
- What are the big 7 of whole brain teaching?
- What are the 5 virtues of whole brain teaching?
- What is the whole brain teaching?
What is the rule #1 in whole brain teaching?
Rule #1 in Whole Brain Teaching is often referred to as the “Class-Yes” rule. It is a simple but powerful technique used to gain the attention and focus of students. When the teacher says “Class,” students respond with a resounding “Yes!” This call-and-response technique helps create an atmosphere of active engagement and signals to students that it’s time to listen and participate in the lesson. Rule #1 sets the stage for effective communication and establishes a positive classroom environment where learning can thrive.
What are the big 7 of whole brain teaching?
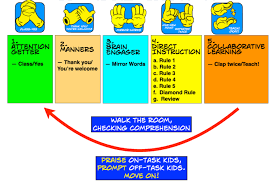
The Big 7 of Whole Brain Teaching are seven key strategies that form the foundation of the Whole Brain Teaching approach. These strategies are designed to engage students, promote active learning, and create a positive classroom environment. Here are the Big 7 of Whole Brain Teaching:
- Class-Yes: This strategy is used to gain students’ attention and establish a cooperative learning environment. The teacher says “Class” and students respond with “Yes” in unison. It helps to quickly refocus the class and create a sense of unity.
- Mirror: The Mirror technique involves students mirroring or repeating instructions, gestures, or information back to the teacher or their peers. This strategy promotes active listening, reinforces understanding, and encourages participation.
- Teach-Okay: Teach-Okay is a cooperative learning strategy where students take turns teaching each other in pairs or small groups. One student becomes the teacher and explains a concept or skill while their partner actively listens and responds with “Okay.” This technique reinforces understanding and allows students to practice explaining concepts in their own words.
- Scoreboard: The Scoreboard is a visual representation of student behavior and engagement in the classroom. It can be a whiteboard, poster, or any other display where points can be added or subtracted based on student behavior or participation. The Scoreboard encourages competition, teamwork, and self-regulation.
- Hands and Eyes: Hands and Eyes is used to quickly gain students’ attention during transitions or when important information is being shared. When the teacher says “Hands,” students raise their hands, and when the teacher says “Eyes,” they make eye contact with the teacher.
- Switch: Switch involves transitioning between different activities or tasks smoothly and efficiently by using cues such as clapping hands or saying “Switch.” This strategy helps maintain momentum during lessons while minimizing disruptions.
- Mighty Groan: Mighty Groan is a playful strategy used to engage students and create a positive classroom atmosphere. When the teacher intentionally makes a mistake or says something silly, students respond with an exaggerated groan. This technique promotes a sense of humor, reduces anxiety, and encourages students to embrace mistakes as part of the learning process.
By incorporating these Big 7 strategies into their teaching practices, educators can foster active learning, student engagement, and a supportive classroom environment that promotes holistic development.
What are the 5 virtues of whole brain teaching?
Whole Brain Teaching emphasizes the development of five key virtues that contribute to a holistic and effective learning experience. These virtues are:
- Attentiveness: Whole Brain Teaching promotes active listening and engagement in the classroom. Students are encouraged to focus their attention on the teacher and their peers, actively participating in discussions and activities. By cultivating attentiveness, students develop better concentration skills and retain information more effectively.
- Responsibility: Whole Brain Teaching encourages students to take ownership of their learning. They are taught to be responsible for their actions, assignments, and behavior in the classroom. This virtue instills a sense of accountability, helping students develop self-discipline and become independent learners.
- Kindness: Creating a positive and supportive classroom environment is essential in Whole Brain Teaching. Teachers emphasize the importance of kindness towards others, promoting empathy, respect, and inclusivity among students. This virtue fosters a sense of community and encourages collaboration among peers.
- Enthusiasm: Whole Brain Teaching believes that enthusiasm is contagious and can greatly impact student engagement and motivation. Teachers are encouraged to exhibit passion for their subject matter, using humor, energy, and excitement to captivate students’ interest. By modeling enthusiasm, educators inspire students to approach learning with curiosity and enthusiasm as well.
- Confidence: Whole Brain Teaching aims to boost students’ confidence by providing immediate feedback and reinforcement during lessons. Teachers create opportunities for students to showcase their understanding through interactive activities or peer teaching moments. This virtue helps students build self-esteem, develop a growth mindset, and become more confident in expressing their ideas.
By nurturing these five virtues – attentiveness, responsibility, kindness, enthusiasm, and confidence – Whole Brain Teaching aims to create a positive learning environment that supports holistic development while enhancing academic achievement. These virtues not only contribute to academic success but also foster essential life skills that empower students beyond the classroom walls.
What is the whole brain teaching?
Whole Brain Teaching (WBT) is an instructional approach that aims to engage and activate all areas of the brain during the learning process. It is a holistic teaching method that incorporates physical movement, gestures, verbalization, and emotional connections to enhance student engagement and promote deeper understanding.
The core principles of Whole Brain Teaching include active participation, immediate feedback, and creating a positive classroom environment. In WBT, students are encouraged to actively participate in their own learning through gestures, movements, and call-and-response activities. This helps stimulate different parts of the brain simultaneously and improves information retention.
Immediate feedback is another important aspect of WBT. Teachers provide instant feedback during lessons to help students gauge their understanding and correct any misconceptions in real-time. This promotes active listening skills and allows for immediate reinforcement of key concepts.
Creating a positive classroom environment is crucial in Whole Brain Teaching. Teachers establish strong relationships with their students by using humor, enthusiasm, empathy, and building a supportive community. This emotional connection enhances student motivation and engagement in the learning process.
Whole Brain Teaching recognizes that individuals have different learning styles and preferences. By engaging both hemispheres of the brain through visual, auditory, and kinesthetic techniques, WBT caters to diverse learners’ needs. This ensures that all students have an opportunity to thrive in the classroom.
Overall, Whole Brain Teaching is an innovative approach that seeks to activate all areas of the brain during instruction. By incorporating movement, gestures, immediate feedback, and emotional connections into lessons, it aims to create a dynamic learning experience that fosters critical thinking skills, enhances retention of information, and promotes holistic development in students.