Network Technology: Connecting the World
In today’s interconnected world, network technology plays a crucial role in facilitating communication, collaboration, and information sharing. From the internet to wireless networks, this technology has revolutionized the way we connect with others and access information. Let’s explore the impact and importance of network technology in our lives.
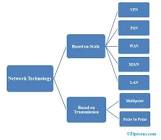
At its core, network technology refers to the infrastructure and systems that enable devices to communicate with each other. It encompasses a wide range of technologies, including local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), wireless networks, and the internet itself. These networks allow computers, smartphones, tablets, and other devices to exchange data and share resources seamlessly.
One of the most significant advancements in network technology is the internet. It has transformed how we access information, communicate with others, conduct business, and even entertain ourselves. The internet connects billions of devices worldwide through a complex web of interconnected networks. It enables us to browse websites, send emails, stream videos, participate in online meetings, and engage in social media platforms.
Wireless networks have also revolutionized our lives by providing us with mobility and convenience. Wi-Fi technology allows us to connect our devices without the need for physical cables. We can now access the internet from anywhere within range of a Wi-Fi network – whether it’s at home, in coffee shops, or even on airplanes. This freedom has empowered us to work remotely, stay connected on-the-go, and enjoy online entertainment wherever we are.
Network technology has also had a profound impact on businesses across various industries. It has enabled organizations to streamline their operations by connecting employees from different locations through virtual private networks (VPNs). This allows for seamless collaboration on projects regardless of geographical barriers.
Moreover, businesses can leverage cloud computing services that rely on network technology to store data remotely and access it from anywhere. This eliminates the need for costly physical servers while ensuring data security and redundancy.
In the healthcare sector, network technology has facilitated the sharing of medical records, enabling healthcare professionals to access patient information quickly and accurately. This has led to improved patient care, reduced errors, and enhanced efficiency in healthcare delivery.
Education has also been transformed by network technology. Online learning platforms have made education more accessible and flexible. Students can now access educational resources, participate in virtual classrooms, and collaborate with peers from around the world. Network technology has opened up new avenues for lifelong learning and professional development.
However, as we rely more on network technology, concerns about security and privacy have become increasingly important. Cybersecurity measures are crucial to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or cyber-attacks. Network administrators employ various techniques such as firewalls, encryption protocols, and intrusion detection systems to safeguard networks and the information transmitted through them.
In conclusion, network technology has become an integral part of our daily lives. It connects us with people across the globe, empowers businesses to operate efficiently, revolutionizes education, and enhances various aspects of our society. As technology continues to evolve rapidly, we can expect further advancements in network technology that will shape our future in ways we can only imagine.
8 Advantages of Network Technology: Boosting Productivity, Cutting Costs, Strengthening Security, Empowering Mobility, Scaling Up, Enhancing Reliability, Elevating Customer Service, and Promoting Data Sharing & Collaboration
- Increased Productivity
- Cost Savings
- Improved Security
- Enhanced Mobility
- Scalability
- Increased Reliability
- Improved Customer Service
- Data Sharing & Collaboration Tools
6 Cons of Network Technology: Exploring Security Risks, Costs, Compatibility Issues, Interference, Limited Scalability, and Reliability Challenges
Increased Productivity
Increased Productivity: How Network Technology Boosts Efficiency
In today’s fast-paced and interconnected work environment, network technology has emerged as a powerful tool for enhancing productivity. By enabling seamless communication and collaboration among employees, network technology streamlines workflows and facilitates efficient task completion. Let’s delve into how this pro of network technology contributes to increased productivity in the workplace.
Effective communication is vital for any organization to thrive. Network technology provides various channels for employees to connect and exchange information rapidly. With email, instant messaging, and video conferencing tools, team members can communicate in real-time regardless of their physical location. This eliminates the need for time-consuming meetings or lengthy email exchanges, allowing for quick decision-making and problem-solving.
Collaboration is another crucial aspect of productivity in the workplace. Network technology provides platforms where employees can work together on projects, share documents, and provide feedback efficiently. Cloud-based storage solutions allow multiple individuals to access and edit files simultaneously, eliminating the need for back-and-forth file transfers or version control issues. This fosters a collaborative environment where ideas can be shared seamlessly, leading to more innovative solutions.
Moreover, network technology enables remote work opportunities. With secure VPN connections, employees can access company resources from anywhere in the world. This flexibility not only promotes work-life balance but also allows organizations to tap into a global talent pool without geographical limitations. Remote work reduces commuting time and distractions often associated with traditional office environments, enabling individuals to focus on their tasks more effectively.
Network technology also facilitates automation and streamlined processes. By connecting various systems within an organization through a network infrastructure, repetitive tasks can be automated, reducing human error and saving valuable time. For instance, data entry processes can be automated through integrated software systems that share information seamlessly across departments.
Furthermore, network technology enables access to vast amounts of information instantly. Employees can conduct online research or access internal databases with just a few clicks. This empowers them with up-to-date information, allowing for more informed decision-making and efficient problem-solving.
However, it is essential to note that while network technology enhances productivity, it also requires proper management and security measures. Network administrators must ensure the reliability and security of the network infrastructure to prevent downtime or data breaches that could hinder productivity.
In conclusion, network technology has revolutionized how employees communicate and collaborate, leading to increased productivity in the workplace. By facilitating efficient communication channels, promoting collaboration, enabling remote work opportunities, automating processes, and providing instant access to information, network technology empowers organizations to achieve more in less time. As businesses continue to adapt and evolve, embracing the benefits of network technology will undoubtedly remain a key driver of productivity in the modern workforce.
Cost Savings
Cost Savings: Streamlining Processes with Network Technology
In today’s fast-paced business environment, organizations are always looking for ways to reduce costs and increase efficiency. One significant advantage of network technology is its ability to streamline processes and eliminate the need for manual data entry or paper-based systems. Let’s explore how network technology can help organizations achieve cost savings.
Traditionally, many businesses relied on manual data entry and paper-based systems to record and manage information. This approach was time-consuming, prone to errors, and required significant storage space for physical documents. However, with network technology, organizations can digitize their processes and automate data entry tasks.
By implementing networked systems such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) software or customer relationship management (CRM) tools, businesses can collect and store data electronically. This eliminates the need for manual input, reducing human error and saving valuable time. Employees can focus on more strategic tasks rather than spending hours on repetitive data entry.
Furthermore, network technology enables organizations to centralize their data storage in secure servers or cloud-based platforms. This eliminates the need for physical filing cabinets or storage rooms dedicated to storing paper documents. Not only does this save physical space within the organization but also reduces costs associated with document management, such as printing, photocopying, and file maintenance.
The ability to access digitized information quickly through networked systems also improves productivity. Employees no longer have to sift through stacks of papers or search through multiple filing cabinets to find relevant information. With just a few clicks, they can retrieve the required data from a centralized database or cloud storage.
Moreover, network technology facilitates collaboration among team members by providing real-time access to shared files and documents. This eliminates the need for printing multiple copies or sending physical documents back and forth between colleagues. Collaboration becomes seamless as employees can work together on projects simultaneously from different locations.
Another cost-saving aspect of network technology is its impact on communication expenses. Traditional methods of communication, such as phone calls or postal services, often incur significant costs for businesses. However, network technology offers affordable alternatives such as Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) systems and email services. These solutions allow organizations to communicate with clients, partners, and employees worldwide at a fraction of the cost of traditional methods.
Network technology also enables remote work opportunities, which can lead to cost savings for organizations. With the ability to connect to company networks and systems from anywhere with an internet connection, employees can work from home or other remote locations. This reduces overhead costs associated with office space, utilities, and commuting allowances.
In conclusion, network technology offers organizations significant cost-saving opportunities by streamlining processes and eliminating manual data entry or paper-based systems. By digitizing information, centralizing data storage, improving collaboration, and reducing communication expenses, businesses can achieve greater efficiency while minimizing costs. Embracing network technology not only enhances productivity but also contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to business operations.
Improved Security
Improved Security: Safeguarding Sensitive Data with Network Technology
In an era where data breaches and cyber threats are on the rise, network technology offers a powerful solution to enhance security measures and protect sensitive information. With the implementation of firewalls, encryption, and authentication protocols, organizations can fortify their defenses against unauthorized access and safeguard their valuable data.
One of the key advantages of network technology is the ability to deploy firewalls. These software or hardware-based security systems act as a barrier between an organization’s internal network and external networks, such as the internet. Firewalls monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic, analyzing it for potential threats or malicious activity. By establishing rules and filters, firewalls can prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data by blocking suspicious connections or malicious software.
Encryption is another critical security measure offered by network technology. It involves encoding data in such a way that only authorized parties can decipher it using a specific decryption key. By encrypting sensitive information before transmitting it over a network, organizations can ensure that even if intercepted, the data remains unreadable and useless to unauthorized individuals. This adds an extra layer of protection against eavesdropping or unauthorized access.
Authentication protocols are also integral to network security. These protocols verify the identity of users or devices attempting to connect to a network or access certain resources. Common authentication methods include usernames and passwords, biometric identifiers like fingerprints or facial recognition, and digital certificates. By implementing strong authentication measures, organizations can ensure that only authorized individuals gain access to their networks and sensitive data.
The improved security provided by network technology has far-reaching implications for businesses across all industries. It helps prevent data breaches that could lead to financial losses, reputational damage, legal complications, and loss of customer trust. By protecting customer information, trade secrets, financial records, and other proprietary data from unauthorized access or theft, organizations can operate with confidence in today’s digital landscape.
Moreover, enhanced security measures enable organizations to comply with industry-specific regulations and standards. Many sectors, such as healthcare, finance, and government, have stringent data protection requirements. By implementing robust security measures provided by network technology, organizations can meet these compliance obligations and avoid penalties or legal consequences.
However, it is important to note that security is an ongoing process. Network administrators must stay vigilant and keep up with evolving threats by regularly updating security protocols, patching vulnerabilities, and educating employees about best practices for data protection. Additionally, conducting regular security audits and penetration testing can help identify potential weaknesses in the network infrastructure.
In conclusion, the improved security offered by network technology is a significant advantage for organizations in today’s digital landscape. By deploying firewalls, encryption techniques, and authentication protocols, businesses can protect their sensitive data from unauthorized access or theft. This not only helps mitigate risks but also ensures compliance with industry regulations while maintaining the trust of customers and stakeholders. With the constant evolution of cyber threats, investing in robust network security measures is essential for organizations to thrive in a digitally connected world.
Enhanced Mobility
Enhanced Mobility: Embracing the Power of Network Technology
In today’s fast-paced world, the ability to access information on the go has become a necessity. Thanks to network technology, this has become a reality. One of the significant advantages of network technology is enhanced mobility, which allows users to access information from virtually anywhere with internet access, providing greater flexibility in the workplace.
Gone are the days when work was confined to a physical office space. With network technology, professionals can now work remotely, breaking free from the constraints of traditional office environments. Whether it’s working from home, a coffee shop, or while traveling, network technology empowers individuals to stay connected and productive regardless of their physical location.
The advent of wireless networks and mobile devices has been instrumental in enabling this enhanced mobility. Wi-Fi networks have become ubiquitous in public spaces and private residences alike. This means that as long as there is Wi-Fi availability, individuals can connect their laptops, smartphones, or tablets to access work-related resources and collaborate with colleagues seamlessly.
The flexibility provided by enhanced mobility allows for better work-life balance. Professionals no longer need to be tied down to their desks for extended hours. They can choose where and when they work best, resulting in increased productivity and job satisfaction.
Moreover, network technology enables real-time collaboration among team members located in different parts of the world. Through virtual meetings and online project management tools, professionals can collaborate on projects regardless of geographical barriers. This not only saves time but also fosters teamwork and innovation.
Enhanced mobility also benefits businesses by expanding their talent pool beyond local boundaries. With network technology enabling remote work options, organizations can tap into global talent pools without being limited by geographical constraints. This opens up opportunities for diverse perspectives and expertise that can drive business growth and success.
However, it’s important to note that enhanced mobility comes with its own set of challenges. Security concerns such as data breaches or unauthorized access become more critical when employees access company information from outside the traditional office environment. It is vital for businesses to implement robust security measures, such as VPNs and encryption protocols, to protect sensitive data and ensure secure remote access.
In conclusion, enhanced mobility made possible by network technology has revolutionized the way we work. It has given professionals the freedom to work from anywhere, collaborate seamlessly, and achieve a better work-life balance. By embracing this pro of network technology, individuals and businesses can harness its power to stay connected, productive, and competitive in today’s dynamic and ever-evolving digital landscape.
Scalability
Scalability: Empowering Organizations to Grow and Adapt
In the ever-changing landscape of business, scalability is a crucial factor for success. With the advent of network technology, organizations now have the ability to easily scale their networks up or down based on their needs at any given time. This flexibility eliminates the need for purchasing additional hardware or software licenses, saving both time and resources.
Traditionally, scaling a network meant investing in new infrastructure, such as servers, switches, and routers. This process could be time-consuming and expensive, especially for growing businesses with limited budgets. Network technology has revolutionized this process by allowing organizations to scale their networks effortlessly.
One of the key advantages of network technology is its ability to accommodate increased traffic and data flow without requiring significant hardware upgrades. By leveraging virtualization techniques and cloud-based services, organizations can expand their network capacity without physically adding more devices or servers. This scalability ensures that businesses can meet the demands of a growing user base or handle increased data volume without disruptions.
On the other hand, organizations can also scale down their networks when necessary. For example, during periods of reduced activity or budget constraints, they can temporarily reduce network resources without incurring unnecessary expenses. This flexibility allows businesses to optimize their network usage based on fluctuating needs while maintaining efficiency.
The scalability offered by network technology also extends to software applications and licenses. With traditional systems, adding new users often required purchasing additional software licenses at considerable costs. However, with modern network technologies such as cloud computing and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), organizations can easily scale up or down their software usage based on demand. They can add or remove user accounts as needed without the hassle of managing physical installations or purchasing additional licenses.
Moreover, network technology enables organizations to quickly adapt to changing market conditions and business requirements. In today’s fast-paced world, businesses need agility to respond promptly to evolving customer needs and market trends. By leveraging scalable network solutions, organizations can swiftly adjust their infrastructure and resources to align with changing demands, giving them a competitive edge.
In conclusion, the scalability provided by network technology is a significant advantage for organizations. It allows businesses to easily expand or contract their networks based on demand, without the need for extensive hardware investments or software license purchases. This flexibility empowers organizations to grow, adapt, and optimize their operations efficiently. As technology continues to advance, scalability will remain a critical factor in driving business success in the dynamic digital landscape.
Increased Reliability
Increased Reliability: The Backbone of Resilient Systems
In the digital age, organizations rely heavily on network technology to keep their operations running smoothly. One significant advantage of network technology is its ability to enhance reliability. By implementing redundant connections and failover protocols, businesses can ensure that their systems remain available even in the face of technical issues or natural disasters.
Redundant connections are a key component of a reliable network infrastructure. They involve creating duplicate pathways for data transmission, so if one connection fails, another can seamlessly take over. This redundancy minimizes downtime and ensures uninterrupted communication and access to critical resources.
For example, in a business environment, redundant connections can be established by using multiple internet service providers (ISPs) or setting up backup communication lines such as satellite links or cellular networks. If one ISP experiences an outage or disruption, traffic automatically reroutes through the alternative connection, allowing employees to continue their work without interruption.
Failover protocols further enhance reliability by automatically switching to backup systems when primary components fail. These protocols monitor the health and performance of critical network devices such as servers, routers, and switches. If any device malfunctions or becomes unresponsive, failover protocols kick in to redirect traffic and services to redundant devices.
This level of redundancy not only safeguards against technical glitches but also protects against natural disasters that may cause physical damage to network infrastructure. For instance, if a severe storm damages power lines or network cables in one location, failover protocols can reroute traffic through alternate pathways or data centers located in different regions. This ensures that vital services remain accessible despite localized disruptions.
The increased reliability offered by network technology has far-reaching benefits for organizations across various sectors. In industries such as finance, healthcare, and e-commerce where downtime can result in significant financial losses or compromised customer trust, reliable networks are essential for maintaining seamless operations.
Moreover, increased reliability also translates into improved productivity and customer satisfaction. Employees can continue their work without interruptions, enabling them to meet deadlines and deliver high-quality services. Customers can access online platforms, make transactions, and receive support without encountering frustrating service disruptions.
While network technology provides increased reliability, it is important to note that maintaining such robust systems requires ongoing monitoring and proactive management. Regular assessments of network infrastructure, testing failover mechanisms, and ensuring redundancy measures are up-to-date are vital to guaranteeing the continued reliability of the network.
In conclusion, the use of redundant connections and failover protocols in network technology significantly enhances reliability. By mitigating the impact of technical failures or natural disasters, organizations can maintain uninterrupted operations and provide reliable services to their employees and customers. Investing in a resilient network infrastructure is a strategic move that ensures business continuity in an increasingly interconnected world.
Improved Customer Service
Improved Customer Service: Bridging the Gap with Network Technology
In the era of global connectivity, network technology has revolutionized customer service by breaking down barriers of distance and time. With tools like VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) and video conferencing, businesses can now provide faster response times and personalized service experiences to customers, regardless of their location or time zone differences.
Traditionally, customer service interactions were limited to phone calls or in-person visits. These methods often involved delays, long wait times, and limited availability. However, network technology has transformed this landscape by enabling businesses to connect with customers in real-time through voice and video communication.
VoIP technology allows businesses to make calls over the internet instead of traditional telephone lines. This means that customer service representatives can handle inquiries from anywhere with an internet connection. Whether it’s a small startup or a multinational corporation, companies can now establish virtual call centers that operate globally without the need for physical infrastructure.
Video conferencing takes customer service to another level by enabling face-to-face interactions between customers and representatives. This technology allows for visual cues, body language interpretation, and a more personal touch that enhances the overall customer experience. It breaks down geographical barriers and fosters a sense of connection that was previously limited to in-person interactions.
By leveraging these network technologies, businesses can provide faster response times to customer queries. No longer constrained by physical locations or time zones, companies can ensure that customers receive timely assistance regardless of where they are located in the world. This level of responsiveness enhances customer satisfaction and builds trust in the brand.
Moreover, network technology enables businesses to offer personalized service experiences. Through data analytics and CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems integrated with their network infrastructure, companies can gather valuable information about individual customers’ preferences and history. This allows representatives to tailor their interactions accordingly, providing personalized recommendations or resolving issues based on past interactions.
The benefits of improved customer service through network technology extend beyond individual interactions. Businesses can also leverage these tools to conduct virtual training sessions, webinars, and workshops for customers. This not only enhances knowledge sharing but also allows for a more interactive and engaging learning experience.
However, it is important to note that while network technology has greatly improved customer service, it is essential for businesses to maintain a balance between automation and human interaction. While automated systems can handle routine inquiries efficiently, there are instances where human touch and empathy are crucial in resolving complex issues or providing emotional support.
In conclusion, network technology has transformed customer service by eliminating geographical barriers, reducing response times, and enabling personalized experiences. By embracing tools like VoIP and video conferencing, businesses can provide exceptional service regardless of location or time zone differences. As technology continues to advance, the possibilities for enhancing customer service through network technology will only continue to grow.
Data Sharing & Collaboration Tools
Data Sharing & Collaboration Tools: Enhancing Productivity and Connectivity
In today’s fast-paced and interconnected world, efficient data sharing and seamless collaboration are essential for organizations to thrive. Network technology has revolutionized these aspects by providing a wide range of tools that enable users to share files and collaborate on projects in real-time, regardless of their physical location. Let’s explore the benefits of these data sharing and collaboration tools made possible by network technology.
One of the key advantages of network technology is the ability to share files quickly and easily. Shared drives, cloud storage solutions, and file-sharing platforms have become indispensable tools in modern workplaces. These platforms allow users within an organization to store files centrally, making them accessible to authorized individuals from any device connected to the same network.
This accessibility eliminates the need for physical storage devices or cumbersome email attachments, streamlining the sharing process. Users can upload files to shared drives or cloud storage solutions, instantly making them available for others to view, edit, or download. This not only saves time but also ensures that everyone has access to the most up-to-date version of a document.
Real-time collaboration is another significant advantage facilitated by network technologies. Instant messaging platforms and collaborative software enable teams to work together seamlessly on projects regardless of their physical location. Through these tools, team members can communicate in real-time, exchange ideas, provide feedback, and make decisions collectively.
Collaborative software often includes features such as document editing in real-time, shared task lists, project management dashboards, and video conferencing capabilities. These functionalities foster teamwork and enhance productivity by allowing team members to work together efficiently without being physically present in the same location.
Moreover, network technology enables remote work possibilities. With data sharing and collaboration tools accessible from any device connected to the network, employees can work from home or other remote locations while staying connected with their colleagues. This flexibility not only promotes work-life balance but also allows organizations to tap into a global talent pool without geographical limitations.
The benefits of data sharing and collaboration tools extend beyond organizational boundaries as well. Network technology enables seamless collaboration with external partners, clients, and suppliers. Secure file-sharing platforms and virtual meeting tools facilitate communication and collaboration across organizations, fostering stronger relationships and accelerating project timelines.
However, it is essential to prioritize data security when using these tools. Organizations must implement robust security measures to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access or data breaches. Encryption protocols, access controls, and regular security audits are crucial in maintaining the integrity of shared data.
In conclusion, network technology has revolutionized the way organizations share data and collaborate on projects. Through shared drives, cloud storage solutions, instant messaging platforms, and more, users can quickly share files and collaborate in real-time from any device connected to the same network. These tools enhance productivity, foster teamwork, enable remote work possibilities, and facilitate collaboration with external partners. As network technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative solutions that will further enhance connectivity and productivity in the workplace.
Security risks
Security Risks: The Dark Side of Network Technology
While network technology has undoubtedly transformed the way we communicate and access information, it is not without its drawbacks. One significant concern associated with network technology is the increased vulnerability to security risks. Networks, whether local or global, can become targets for cyber attacks, malware, and other malicious activities.
In today’s digital landscape, cybercriminals are constantly devising new ways to exploit network vulnerabilities for their gain. They may attempt to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data, disrupt operations, or steal valuable information. These attacks can have severe consequences for individuals, businesses, and even governments.
One common form of attack is a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack. In this scenario, a network is flooded with an overwhelming amount of traffic from multiple sources simultaneously. This flood of traffic overwhelms the network’s capacity and renders it inaccessible to legitimate users. DDoS attacks can disrupt online services, cripple websites, and cause financial losses for businesses.
Malware is another security risk associated with networks. Malicious software such as viruses, worms, ransomware, and spyware can infiltrate networks through various means like email attachments or malicious downloads. Once inside a network, malware can wreak havoc by corrupting files, stealing sensitive information like passwords or financial data, or even taking control of devices.
Phishing attacks are yet another prevalent threat in the digital realm. Phishing involves tricking individuals into revealing their personal information such as usernames and passwords by posing as a trustworthy entity through emails or fake websites. These stolen credentials can then be used to gain unauthorized access to networks and compromise security.
To mitigate these risks, organizations must implement robust security measures. Firewalls act as a barrier between internal networks and external threats by monitoring incoming and outgoing traffic and blocking suspicious activity. Antivirus software helps detect and remove malware from devices connected to the network.
Regular security updates are crucial in addressing vulnerabilities in network devices and software. Patching known security flaws can prevent cybercriminals from exploiting them. Additionally, strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and user education about phishing and other social engineering techniques are essential in preventing unauthorized access.
Network administrators must also stay vigilant by monitoring network traffic for any unusual activity or signs of intrusion. Intrusion detection systems and log analysis can help identify potential threats and respond promptly to minimize damage.
While network technology provides countless benefits, it is essential to acknowledge the security risks that come along with it. By understanding these risks and implementing appropriate security measures, we can navigate the digital landscape more safely and protect our networks from malicious actors seeking to exploit vulnerabilities.
Cost
Cost: The Hidden Challenge of Network Technology
While network technology has undoubtedly revolutionized the way we connect and communicate, it is not without its drawbacks. One significant con that often goes unnoticed is the cost associated with setting up and maintaining a network.
The expenses related to network technology can quickly add up. First and foremost, there are hardware costs. Building a network requires routers, switches, servers, cables, and other networking equipment. These components can be quite expensive, especially for larger networks or organizations with complex requirements.
Software costs are another consideration. Network operating systems, security software, monitoring tools, and other software licenses can significantly contribute to the overall expenses. Additionally, software updates and licenses may need to be renewed periodically to ensure optimal performance and security.
Personnel costs also play a significant role in the overall expense of network technology. Organizations need skilled professionals who specialize in network administration to set up, configure, monitor, and troubleshoot the network infrastructure. Hiring and retaining qualified personnel can be costly, especially as demand for network administrators continues to rise.
Moreover, ongoing maintenance costs cannot be overlooked. Networks require regular monitoring, updates, backups, and security patches to ensure smooth operation and protect against potential vulnerabilities or threats. These tasks often require dedicated personnel or outsourcing to specialized IT service providers.
For small businesses or organizations with limited financial resources, the cost of implementing network technology can pose a significant challenge. It may require careful budgeting and prioritization of needs to strike a balance between functionality and affordability.
However, it’s important to note that while the upfront costs may seem daunting at first glance, investing in a robust network infrastructure can yield long-term benefits. A reliable network enhances productivity by enabling efficient communication and collaboration among employees. It also provides access to valuable resources such as cloud services or centralized data storage.
To mitigate the cost challenge associated with network technology implementation and maintenance, organizations can explore alternative options such as cloud-based networking solutions or outsourcing network management to specialized service providers. These approaches can help alleviate some of the financial burdens while still reaping the benefits of a well-designed and maintained network.
In conclusion, the cost of setting up and maintaining a network is an important consideration when implementing network technology. It is essential for organizations to carefully evaluate their needs, budget constraints, and long-term goals before embarking on a network infrastructure project. With proper planning and strategic decision-making, organizations can strike a balance between cost-effectiveness and leveraging the advantages that network technology brings to the table.
Compatibility issues
Compatibility Issues: Navigating the Challenges of Network Technology
While network technology has undoubtedly transformed the way we connect and communicate, it is not without its challenges. One significant con that users often encounter is compatibility issues. Different devices may not always be compatible with each other or the network infrastructure they are trying to connect to. Let’s delve into this issue and explore its implications.
In a world where we rely heavily on various devices, from smartphones to laptops, compatibility issues can be frustrating and hinder our ability to seamlessly connect and share information. This problem arises due to differences in hardware, software, protocols, and standards across different devices and network infrastructures.
For instance, a laptop running on a Windows operating system may face difficulties connecting to a printer that is only compatible with macOS. Similarly, a smartphone using an older version of Bluetooth might struggle to establish a connection with wireless headphones that require a newer Bluetooth version.
Compatibility issues can also arise when attempting to connect devices to different types of networks. For example, an older device may not support the latest Wi-Fi standard used by a particular wireless network. This can result in slower speeds or even complete inability to connect.
These compatibility challenges can be particularly frustrating for individuals who rely on multiple devices or work in environments where collaboration is essential. It can lead to inefficiencies, delays in work processes, and added costs as users may need to invest in additional hardware or software solutions.
Moreover, compatibility issues can pose obstacles for businesses striving for seamless integration across their entire network infrastructure. Incompatibilities between different systems and software applications can hinder data sharing and communication between departments or external partners.
To mitigate compatibility issues, manufacturers and developers strive to establish industry standards and protocols that promote interoperability among devices and networks. However, due to rapid advancements in technology and competing interests among different companies, achieving universal compatibility remains an ongoing challenge.
Individuals facing compatibility issues often resort to troubleshooting methods such as updating drivers or firmware, installing software patches, or seeking assistance from technical support. However, these solutions may not always be straightforward or readily available, and users may need to invest time and effort to resolve compatibility conflicts.
As network technology continues to evolve, it is crucial for users to stay informed about compatibility requirements before investing in new devices or attempting to connect them to existing networks. Conducting thorough research and seeking expert advice can help minimize compatibility issues and ensure a smoother user experience.
In conclusion, compatibility issues pose a conundrum in the realm of network technology. The lack of seamless integration between devices and network infrastructures can hinder productivity, collaboration, and user satisfaction. While efforts are made to establish standards and protocols for interoperability, users must remain vigilant and proactive in navigating these challenges. By staying informed and seeking appropriate solutions, we can work towards minimizing compatibility issues and maximizing the potential of network technology in our daily lives.
Interference
Interference: A Challenge in Network Technology
In the world of network technology, one of the significant challenges that users often encounter is interference. Interference occurs when other radio signals in the area disrupt or obstruct the network signal, leading to slowdowns or even disconnections. Let’s delve into this con of network technology and explore its impact.
With the increasing number of wireless devices and networks operating simultaneously, the airwaves have become crowded with various signals. Wi-Fi routers, Bluetooth devices, cordless phones, microwaves, and even neighboring Wi-Fi networks can all contribute to interference. These signals can interfere with each other, causing disruptions in network connectivity.
One common consequence of interference is a decrease in network speed. When multiple signals compete for limited bandwidth, data transmission can become slower and less efficient. This can lead to frustratingly slow internet browsing speeds, buffering while streaming videos or online gaming, and delays in file transfers.
Interference can also result in intermittent connectivity issues or complete disconnections from the network. Devices may experience sudden drops in signal strength or lose connection altogether due to conflicting radio frequencies. This disruption can be particularly problematic for critical tasks such as video conferences or online gaming sessions where a stable connection is crucial.
Several factors contribute to interference, including physical barriers like walls and floors that impede signal propagation. The distance between a device and its access point also plays a role; as devices move further away from the source, they are more susceptible to interference from other signals.
Fortunately, there are steps that users can take to mitigate interference issues. One option is to change the channel on which their Wi-Fi operates. Most routers allow users to select different channels within their frequency range to avoid overlapping with neighboring networks. Additionally, positioning routers away from potential sources of interference such as cordless phones or microwave ovens can help minimize disruptions.
Advanced technologies like beamforming and mesh networks have also emerged as solutions for combating interference. Beamforming focuses the Wi-Fi signal towards connected devices, enhancing signal strength and reducing interference. Mesh networks, on the other hand, utilize multiple access points throughout a space to create a seamless network with improved coverage and reduced interference.
While interference remains a con of network technology, it is important to note that advancements in networking equipment and protocols continue to address these challenges. As technology evolves, we can anticipate improvements in signal stability and increased resistance to interference.
In conclusion, interference poses a significant challenge in network technology, impacting the speed and reliability of wireless connections. However, by understanding the causes of interference and employing strategies to minimize its effects, users can enhance their network performance and enjoy smoother connectivity experiences.
Limited scalability
Limited Scalability: A Challenge of Network Technology
While network technology has brought about numerous benefits and advancements, it is not without its challenges. One such drawback is the limited scalability of networks, which can negatively impact performance when the number of users exceeds a certain threshold.
Scalability refers to a network’s ability to handle an increasing number of users, devices, or data traffic without compromising performance. Networks are designed with specific capacities and limitations, and when these limits are exceeded, issues can arise.
As more users join a network and demand more resources, such as bandwidth or processing power, the network may struggle to meet these increased demands. This can result in slower data transfer speeds, increased latency, and reduced overall efficiency.
The limited scalability of networks becomes particularly evident in scenarios where there is a sudden surge in user activity or when organizations experience rapid growth. For example, during peak hours or major events that generate high network traffic, users may experience delays or disruptions in accessing online services.
In addition to performance issues, limited scalability can also pose challenges for businesses that need to expand their networks to accommodate a growing user base. Scaling up network infrastructure requires investments in additional equipment, upgrades to existing systems, and careful planning to ensure seamless integration. These endeavors can be time-consuming and costly.
However, it is important to note that advancements in network technology have addressed some of these scalability limitations. For instance, the development of cloud computing has allowed businesses to scale their operations by utilizing virtual resources hosted on remote servers. Cloud-based solutions offer flexibility and adaptability by allowing organizations to increase or decrease their resource allocation as needed.
Furthermore, the emergence of software-defined networking (SDN) has introduced more dynamic and flexible approaches to managing networks. SDN enables centralized control over network configurations and allows for easier scaling by separating the control plane from the data plane.
Despite these advancements, scalability remains an ongoing concern for network administrators and organizations alike. It requires careful planning, regular monitoring, and proactive measures to ensure that networks can accommodate growing demands effectively.
In conclusion, limited scalability is a con of network technology that can impact performance and hinder the ability of networks to handle increasing user demands. However, with ongoing advancements in technology and innovative solutions, network scalability challenges are being addressed to provide more efficient and adaptable network infrastructures.
Reliability issues
Reliability Issues: Navigating Network Outages
While network technology has undoubtedly transformed the way we connect and communicate, it also comes with its own set of challenges. One significant con that organizations and individuals face is the issue of reliability. Network outages can occur unexpectedly, causing disruptions in productivity and operations.
Network outages can stem from various factors, such as power outages, hardware failure, natural disasters, or even human error. When these events happen, the connectivity between devices and systems can be severed, leading to a loss of communication and access to critical resources.
One common cause of network outages is power outages. When electricity is disrupted, network infrastructure components like routers, switches, and servers may lose power. Without a stable power supply or backup systems in place, the entire network can go offline temporarily or even for an extended period. This can result in halted operations, interrupted communication channels, and delayed access to vital information.
Hardware failure is another factor that can contribute to network reliability issues. Network devices are susceptible to wear and tear over time. If a critical component fails or malfunctions unexpectedly, it can disrupt the flow of data within the network. This disruption not only affects productivity but also requires time and resources to diagnose and fix the problem.
Unforeseen circumstances like natural disasters or accidents can also have a severe impact on network reliability. Events such as earthquakes, floods, fires, or even construction accidents can damage physical infrastructure like cables or data centers. These incidents can lead to widespread network outages that affect multiple users or organizations simultaneously.
The consequences of network outages are far-reaching. Businesses heavily reliant on network technology may experience financial losses due to downtime and interrupted operations. Employees may be unable to access critical systems or collaborate effectively with their colleagues during an outage. Additionally, customer satisfaction may suffer if services are disrupted or delayed.
To mitigate these reliability issues, organizations must invest in robust backup systems and redundancy measures. Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) units and backup generators can help maintain power during outages. Redundant network devices and alternative communication channels can provide backup paths for data transmission.
Regular maintenance, monitoring, and prompt response to hardware failures are also essential to minimize downtime. Network administrators should conduct routine checks, update firmware, and replace aging components to ensure optimal performance.
Furthermore, organizations can consider implementing disaster recovery plans that outline procedures for responding to network outages caused by unforeseen circumstances. These plans may involve data backups, off-site storage, and alternative communication methods to keep operations running smoothly during challenging times.
While reliability issues pose a challenge in network technology, it is important to remember that no system is entirely immune to occasional disruptions. By understanding the potential causes of network outages and taking proactive measures to address them, organizations can minimize the impact of these events and maintain productivity even in the face of unforeseen circumstances.